Treatment
What are the Options for Treating CSID?
For patients with Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency (CSID) who present with gastrointestinal symptoms that warrant intervention, three major treatment options exist:
-
Severe diet restriction
-
Sucraid®
-
Sucraid® with moderate diet restriction
In This Section
Before Sucraid® was available, treatment of CSID consisted of lifelong adherence to a strict sucrose-free diet. However, given the high sucrose content of Western diets, patient compliance with a sucrose-free diet is challenging. Patient noncompliance is often accompanied by chronic gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms and a low body mass index (BMI) that falls below an age-adjusted growth curve.1-3 In a clinical trial observing the response to a restricted diet, up to 75% of patients remained symptomatic, mostly due to noncompliance with the diet.4
Enzyme replacement therapy with Sucraid® offers a pharmacologic alternative to sucrose-free diets. Sucraid® is an effective option for the management of sucrase deficiency and reduces or eliminates the need for dietary restrictions of sucrose and the symptoms associated with CSID in the majority of patients. In a clinical trial, 81% of patients with CSID managed by Sucraid® became asymptomatic, defined as symptom-free for at least 7 of the 10 treatment days.4 Note that Sucraid® does not provide specific replacement therapy for deficient isomaltase.5 Therefore, restricting starch in the diet may still be necessary in order to minimize symptoms. The need for dietary starch restriction in patients using Sucraid® should be evaluated on a patient-by-patient basis.
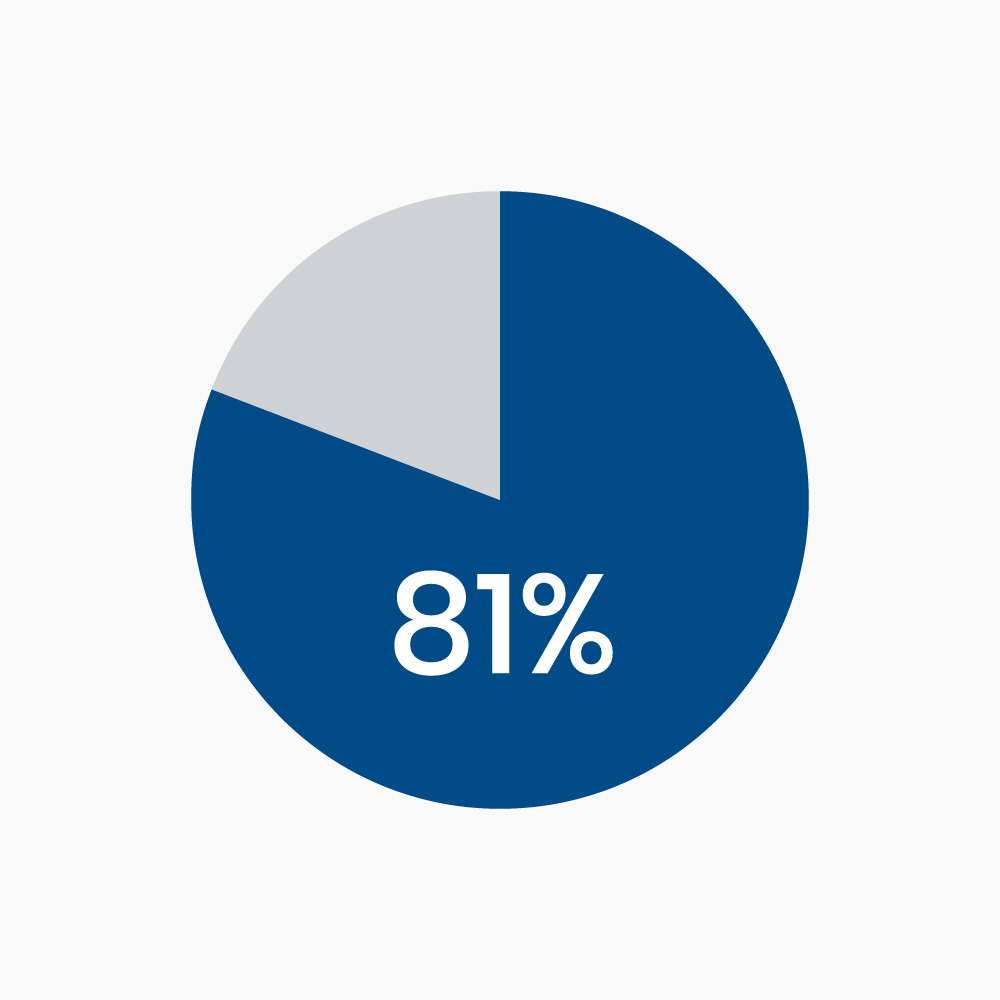
Figure 1. In a long-term clinical trial, 81% of study subjects with CSID who were treated with Sucraid® became asymptomatic, defined as symptom-free for at least 7 of the 10 treatment days.4
References
- Treem WR. Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995;21(1):1-14. doi:10.1097/00005176-199507000-00001
- Gudmand-Høyer E. Sucrose malabsorption in children: a report of thirty-one Greenlanders. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985;4(6):873-877. doi:10.1097/00005176-198512000-00005
- Gudmand-Høyer E, Krasilnikoff PA, Skovbjerg H. Sucrose-isomaltose malabsorption. Adv Nutr Res. 1984;6:233-269. doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-2801-8_9
- Treem WR, McAdams L, Standford L, Kastoff G, Justinich C, Hyams J. Sacrosidase Therapy for Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;28(2):137-42. doi:10.1097/00005176-199902000-00008
- Sucraid® [package insert]. Vero Beach, FL: QOL Medical, LLC; 2024.